Data Modeling Fundamentals
Learn to build proper data models with relationships
What is a Data Model?
A data model defines how your tables connect to each other.
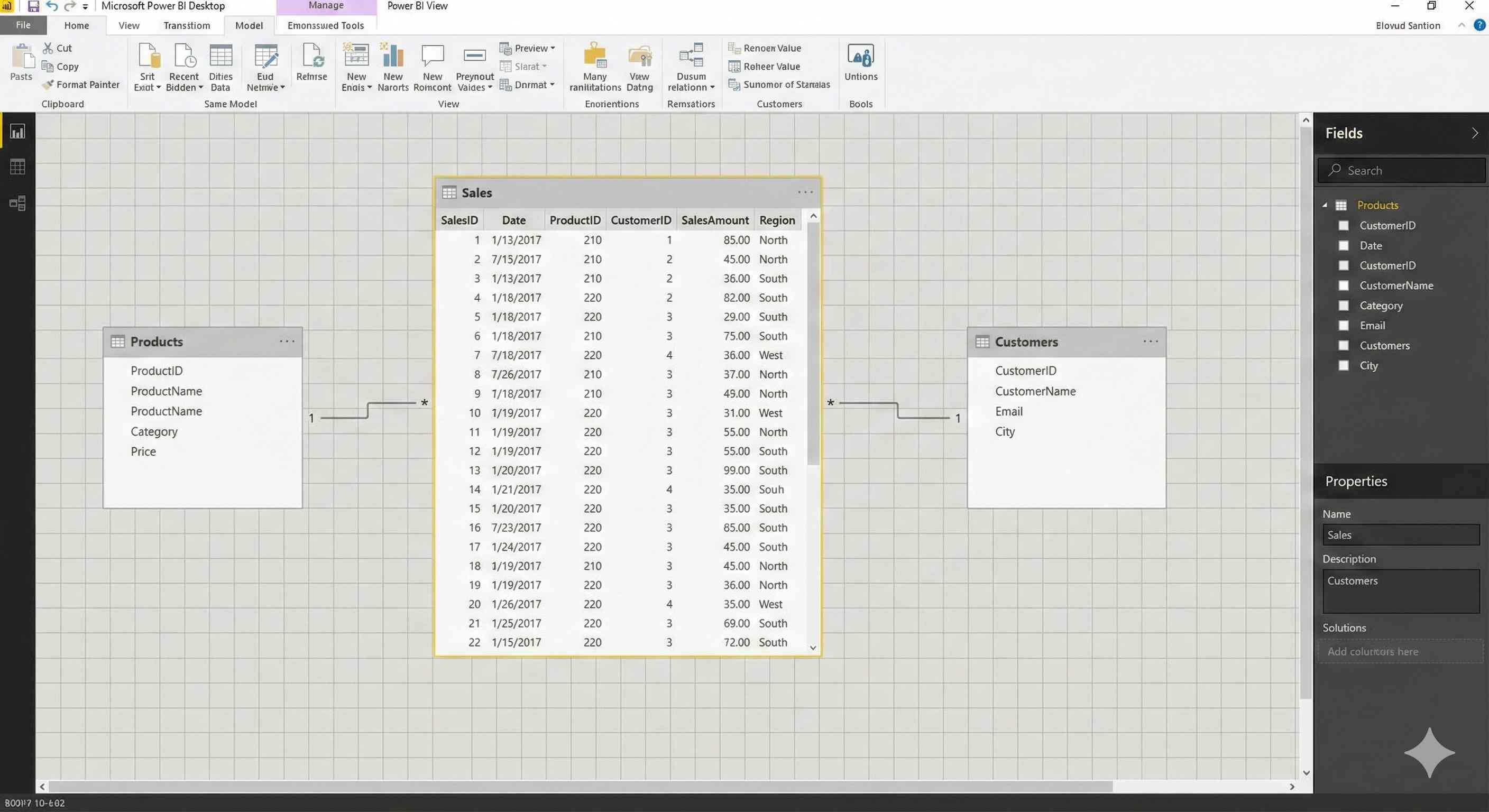
Without relationships, tables are isolated. With relationships, Power BI knows how to combine data automatically.
Star Schema
The best structure for Power BI:
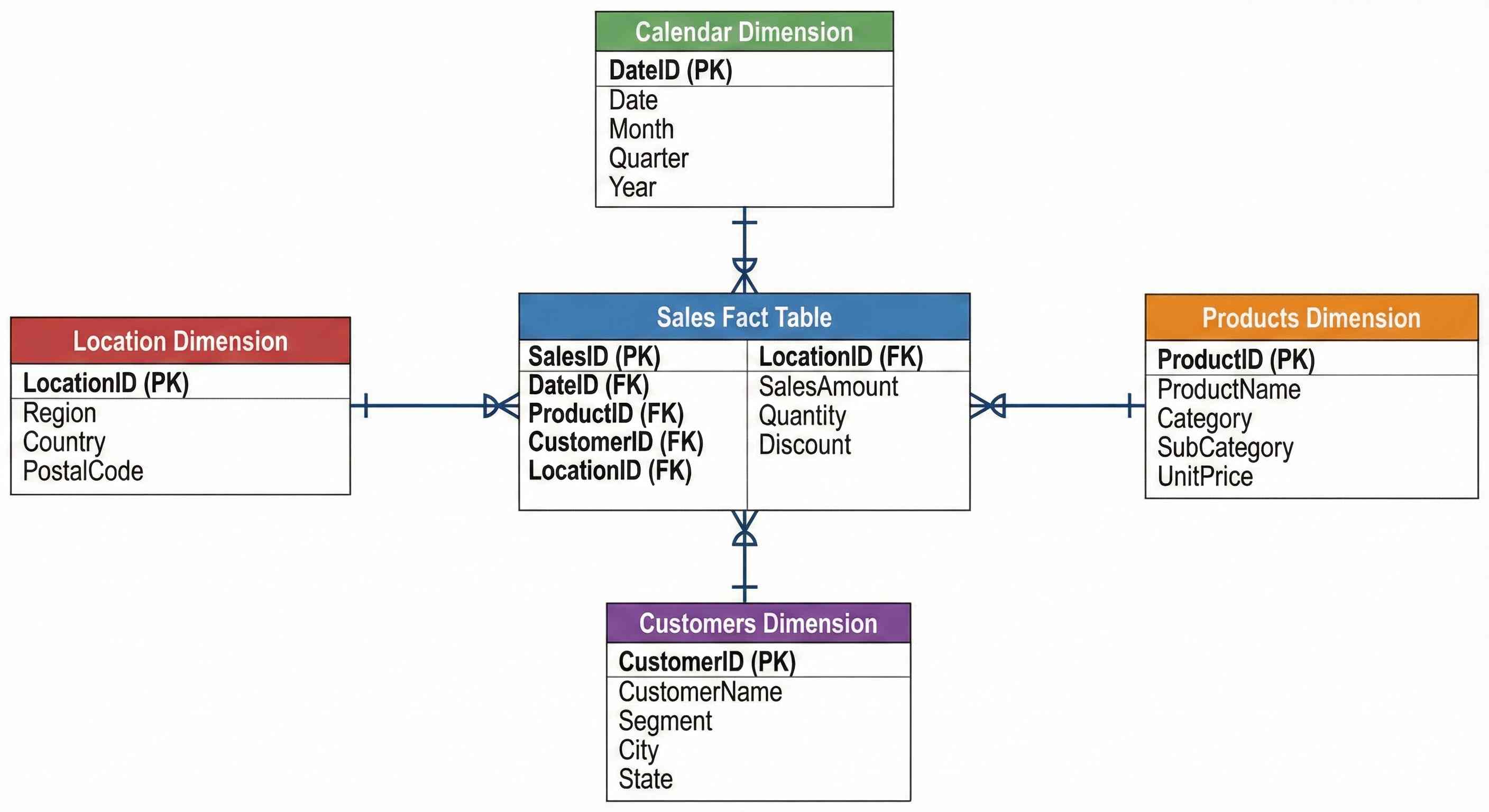
| Table Type | Contains | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Fact (center) | Numbers, transactions | Sales, Orders |
| Dimension (around) | Descriptive data | Products, Customers, Dates |
Creating Relationships
Step 1: The Initial State
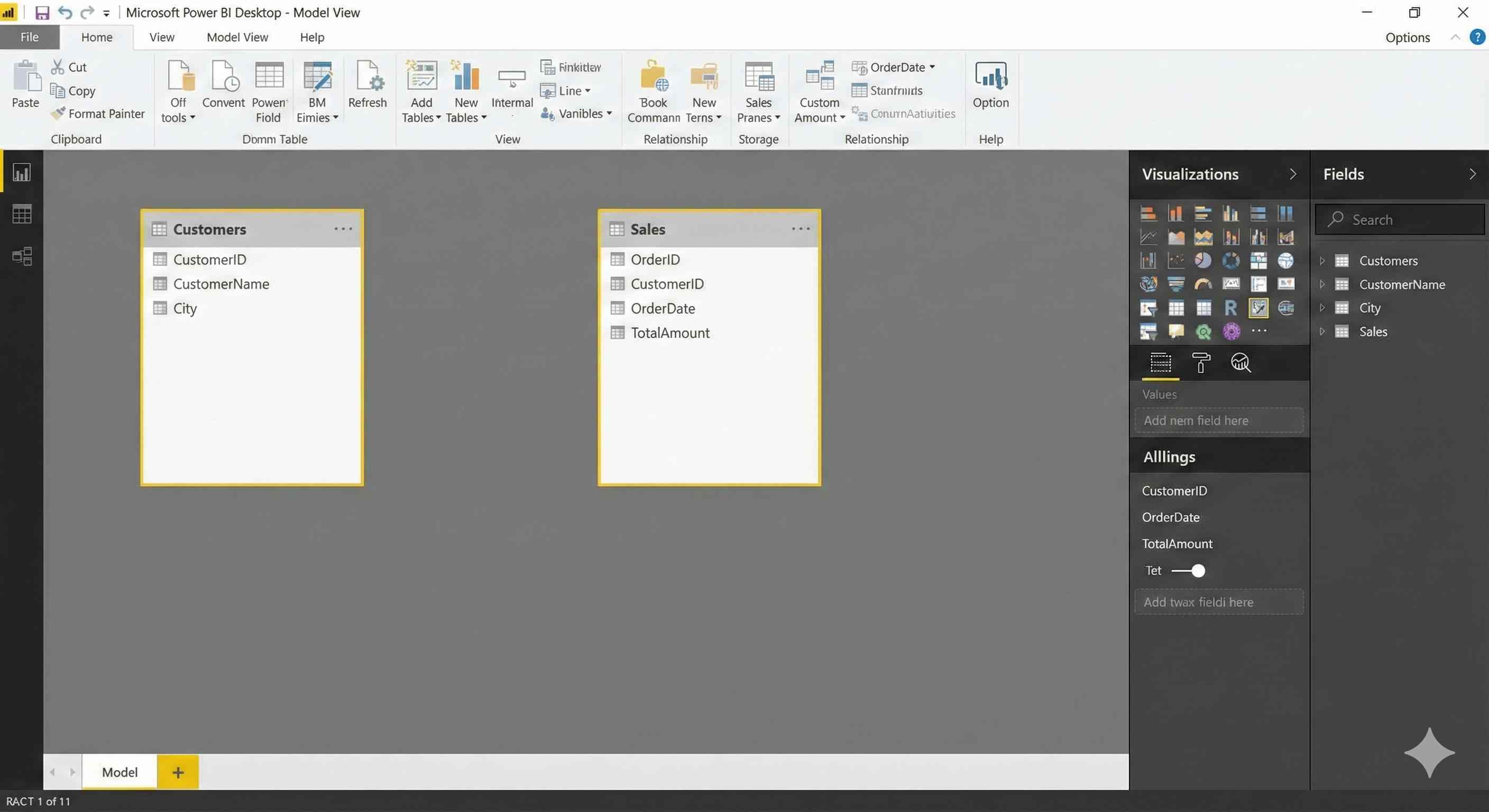
Go to Model View - you'll see your tables but they're not connected yet.
Step 2: Drag to Connect
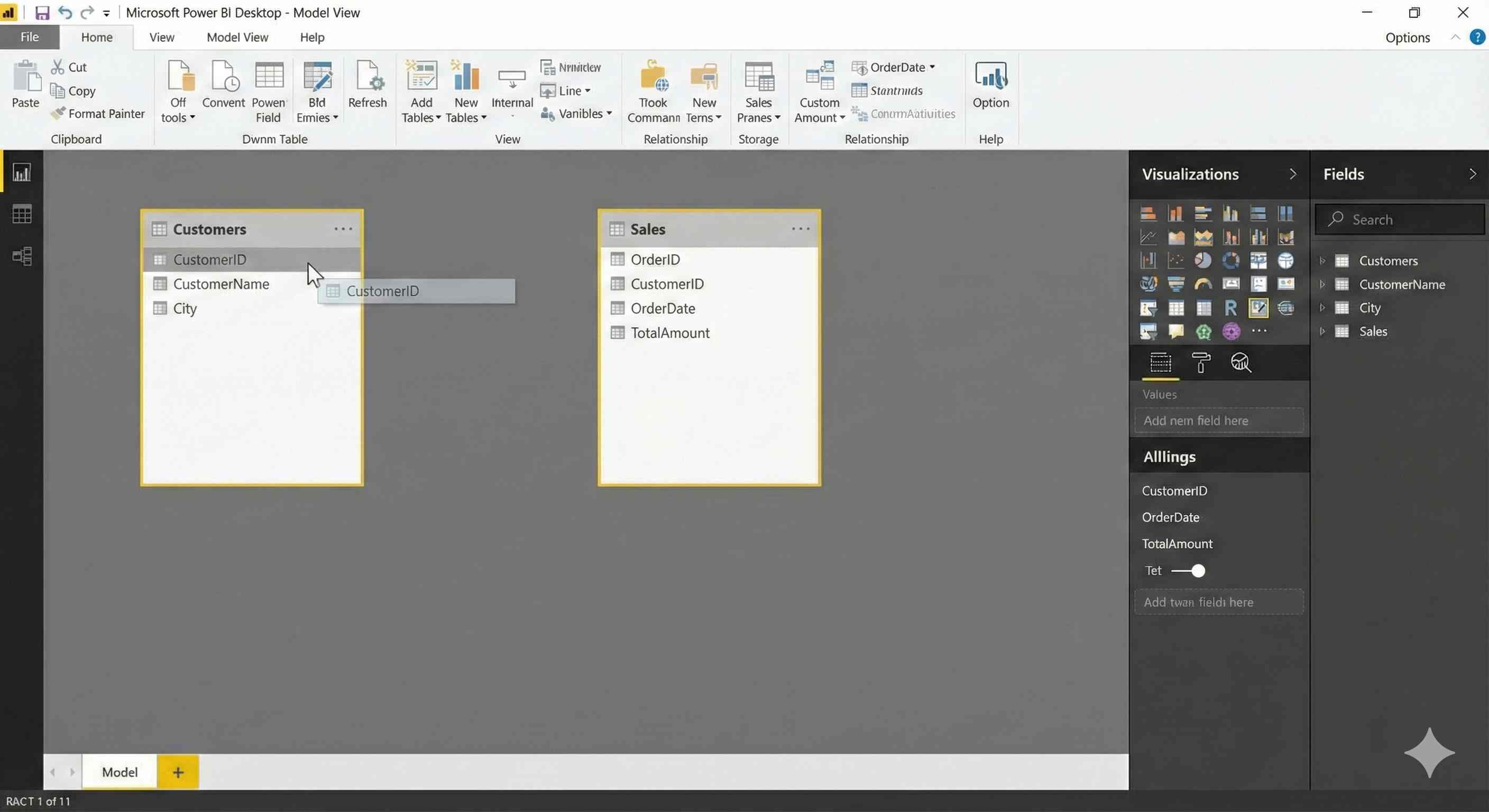
Click on CustomerID in one table and drag it to CustomerID in the other table.
Step 3: Relationship Created
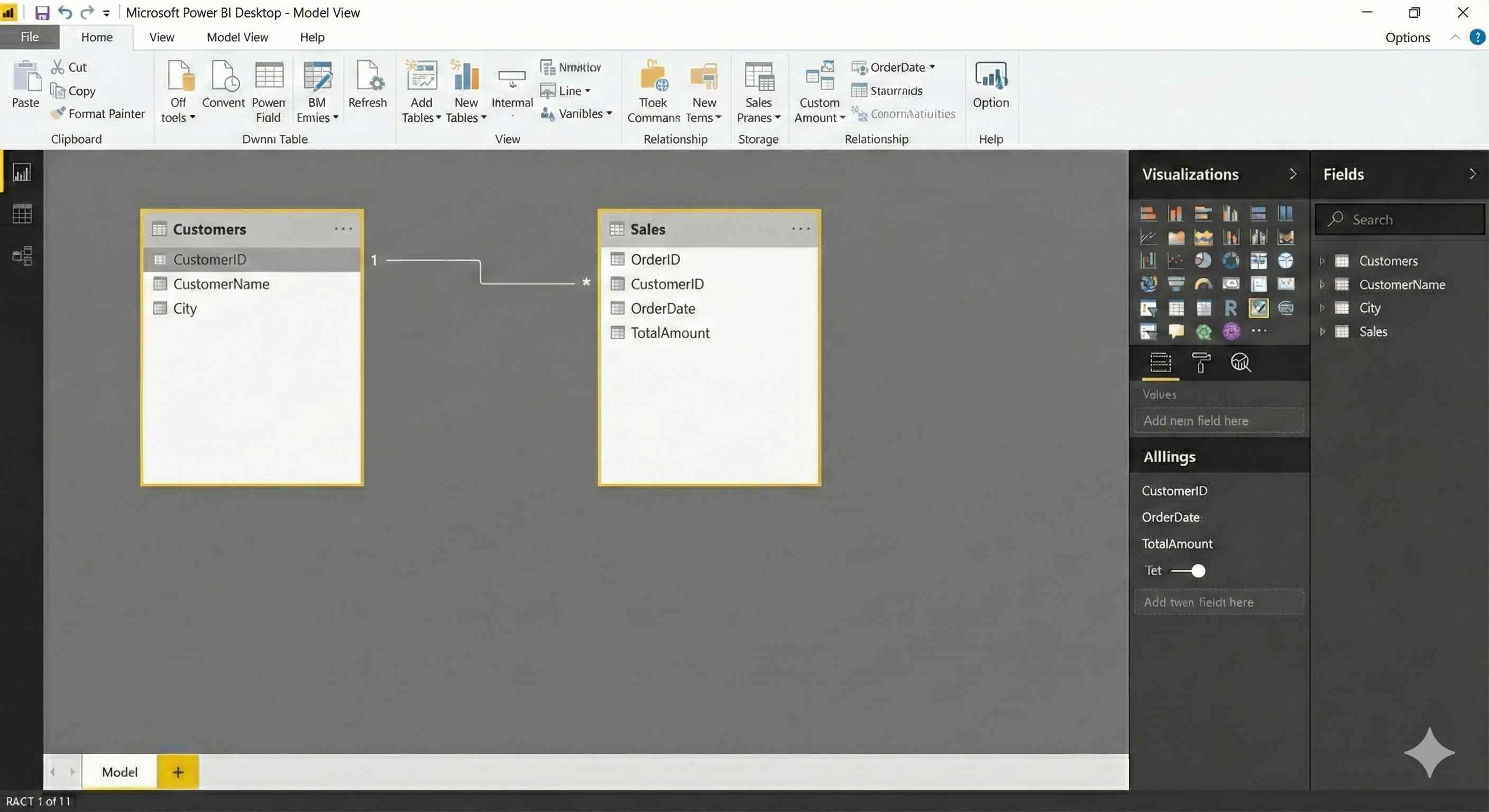
Release the mouse - Power BI creates the relationship line with 1:* symbols.
Cardinality
| Type | Meaning | Use |
|---|---|---|
| One-to-Many (1:*) | One customer has many orders | Most common |
| One-to-One (1:1) | One row matches one row | Rare |
| Many-to-Many (:) | Multiple matches both sides | Avoid |
Keys
Primary Key - Unique ID in dimension table (CustomerID in Customers)
Foreign Key - Reference in fact table (CustomerID in Sales)
Best Practices
- Use ID numbers as keys, not names
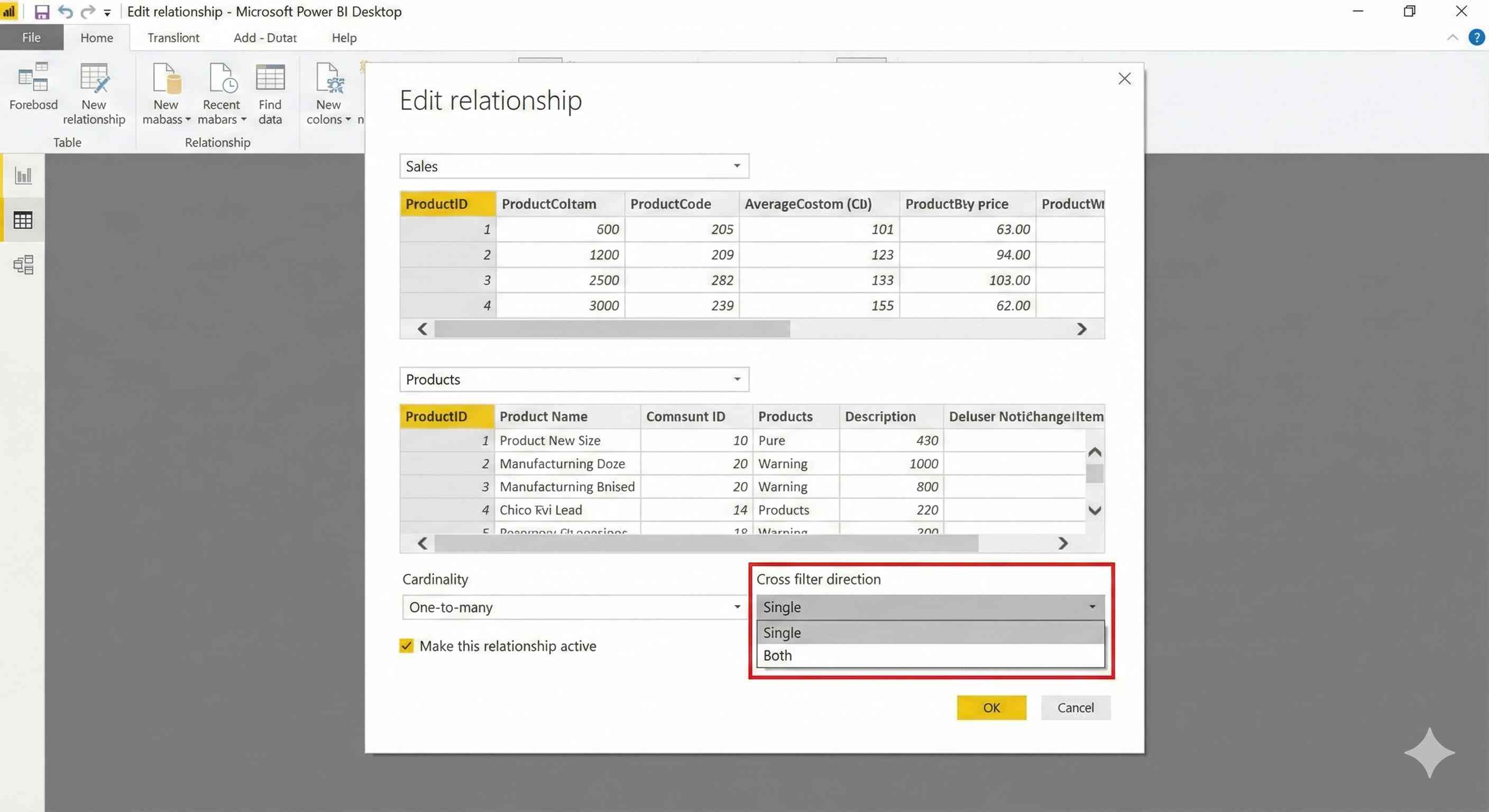
- Keep cross-filter direction as "Single"
- Always create a separate Date/Calendar table
- Follow star schema pattern
Quick Setup
- Import your tables
- Go to Model View
- Drag matching columns to create relationships
- Verify with a visual in Report View
Good data modeling = good reports. Spend time getting this right!